Apps Zone

Exploring the Intricacies of Wireless Surveys
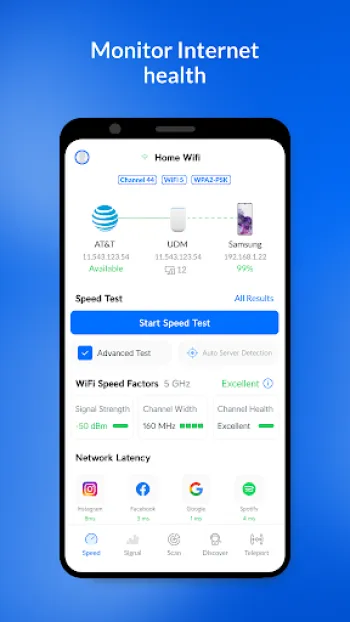
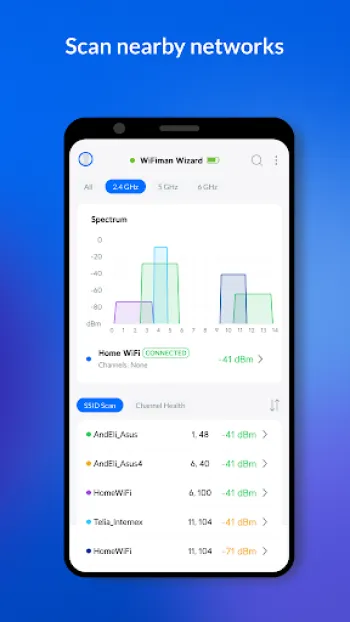
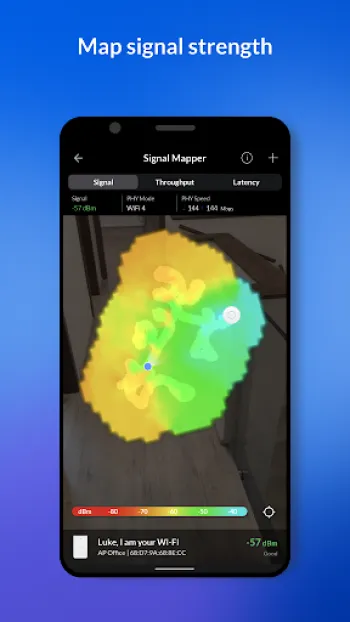
Conducting a wireless survey is crucial for optimizing network performance, identifying coverage gaps, and ensuring seamless connectivity in environments ranging from small offices to sprawling campuses. Wireless networks, unlike their wired counterparts, are influenced by more variable factors such as interference, signal obstructions, and the diverse capabilities of network devices. At the heart of any wireless survey is the measurement of signal strength and quality across different zones, which determines where access points (APs) should be positioned and which frequency channels they should use. Understanding radio frequency (RF) concepts, channel bandwidth, and network topology is fundamental. Successful wireless surveys start by mapping the physical environment, considering factors like building materials which might impede wireless signals, and understanding user density which impacts bandwidth availability. Tools like WiFiman, which integrates sophisticated network detection capabilities, can streamline this process by instantly detecting available WiFi networks and Bluetooth LE devices. Moreover, such tools can help in real-time monitoring of network subnets to gather data on active protocols and potential interference from nearby networks or devices. Conducting a wireless survey involves intricate planning, where one must anticipate future scalability—as user demand grows, so should the network's capability. Advances like WiFi 6 bring improvements, such as increased speed and reduced latency, but these benefits only materialize when a comprehensive wireless survey is conducted to facilitate optimal deployment. As enterprises increasingly rely on wireless connectivity for essential operations, understanding the delicate balance of signal strength, network load, and device compatibility becomes non-negotiable for IT professionals. Through dense analysis using apps like WiFiman, which supports WiFi 6 and advanced features like zero-configuration VPN, enterprises can fine-tune their network settings to provide superior user experiences and maintain robust, interference-free connections.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Wireless Surveys
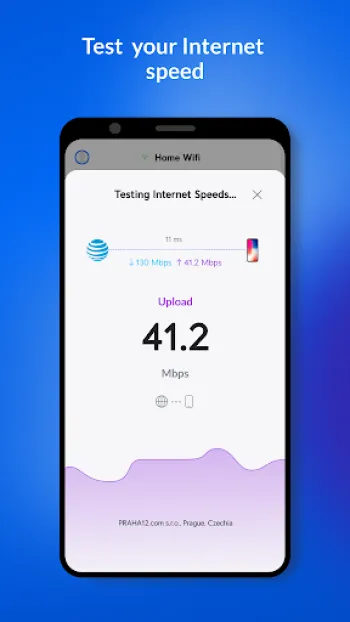
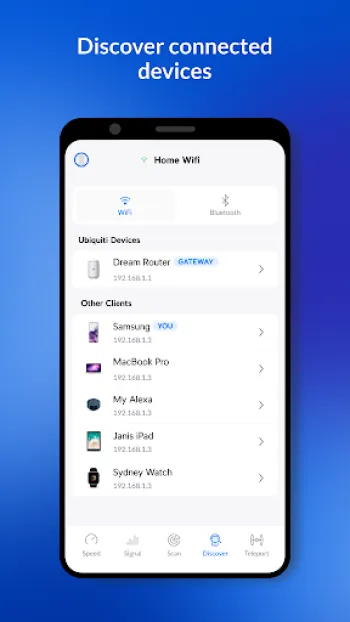
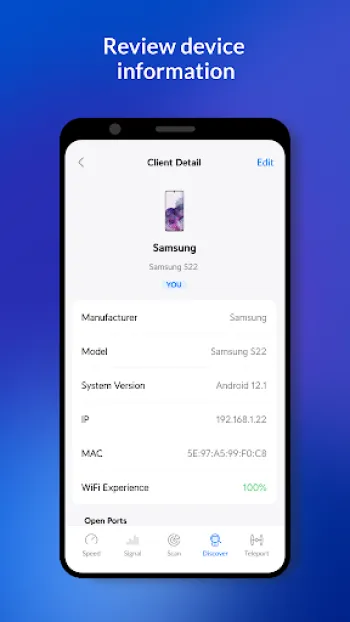
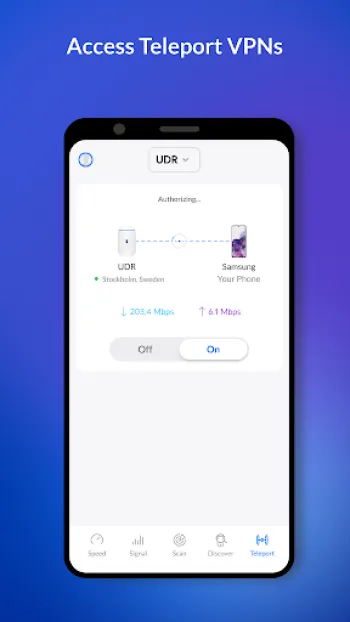
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficacy and accuracy of wireless surveys. Contemporary tools and applications, such as WiFiman, empower network administrators with sophisticated features that enable deeper, more granular insights into network performance. These technologies allow for advanced network scans that reveal intricate details about every detected device, including Bonjour, SNMP, NetBIOS, and Ubiquiti discovery protocols. One compelling feature in modern wireless survey technology is the simulation of network environments that forecast the impact of changes before they are implemented—saving time, reducing downtime, and preempting potential connectivity issues. As technical continuity demands evolve, integration with cloud-based management platforms allows seamless remote access and updates, reducing the need for physical on-site presence. The evolution of mobile technology has extended the reach of network surveys beyond traditional desktop tools. Mobile apps, particularly on Android platforms, provide network testers with on-the-go solutions. For instance, the ability to conduct speed tests, monitor packet loss, and evaluate ping latency directly from a smartphone means problems can be diagnosed and resolved without delay. Additionally, machine learning algorithms, when incorporated, offer predictive analytics that notify admins of deteriorating trends or potential vulnerabilities before they escalate into critical issues. Another significant technological advancement is the incorporation of enhanced data visualization features which translate complex datasets into user-friendly graphs and charts, enabling quicker decision-making and strategic planning. Integrating remote management options, such as Teleport, a free VPN that facilitates remote networking with zero-configuration, adds robust layers of flexibility, convenience, and security. Infrastructures increasingly depend on these advanced technologies to not only conduct the initial survey but also to ensure ongoing monitoring and tweaking, accounting for continuous network changes and demands.
Mastering Wireless Network Configuration and Optimization
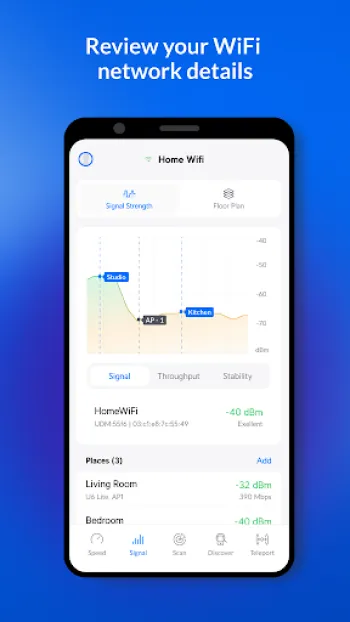
Configuring and optimizing wireless networks is a nuanced task that demands a strong grasp of various technical principles and a strategic approach tailored to specific environmental conditions. During the configuration phase, incorrect settings can lead to issues like signal interference, coverage blackspots, and bandwidth throttling. Optimization starts with selecting the right hardware—one must decide whether to deploy UniFi, AmpliFi, or other Ubiquiti devices depending on the environment's complexity and coverage requirements. Fine-tuning the network involves setting the appropriate channel width and frequency to minimize overlap and interference with neighboring networks; regularly using tools like WiFiman can help to dynamically identify less congested channels ideal for relocation of access points. A meticulous understanding of the network's physical layout is indispensable—sometimes repositioning an access point even slightly can boost performance significantly due to changes in the RF landscape. Furthermore, the relationship between different network segments should be learned; the integration of edge devices like EdgeMAX, EdgeRouter, or EdgeSwitch requires precise configuration settings to enable efficient traffic flow from point A to point B without bottlenecks. Modern solutions also allow more strategic control through software-defined networking (SDN), where centralized management interfaces allow comprehensive control and distribution of network resources. Understanding TCP/IP configurations and DNS settings plays a vital role in reducing latency and boosting overall network throughput. By constantly monitoring and interpreting the obtained data from network analyzers, organizations can ensure not only steady and robust connectivity but also adapt instantly to any challenges thrown their way by a dynamic network landscape. As wireless technology propagates into more sectors, mastering these wireless network configurations becomes paramount for delivering top-tier network performance that meets the evolving demands of users and devices alike.
Technological Advancements in Ubiquiti Devices
Ubiquiti devices represent a leading force in networking technology; their continual evolution illustrates the power of innovation in enhancing wireless connectivity. These devices cater to varying levels of deployments from residential to enterprise-grade solutions with products like UniFi for high-density environments, AmpliFi for home usage, and EdgeMAX for advanced routing and switching. The backbone of Ubiquiti's success lies in their relentless pursuit of improved interface design and technology integration that addresses the multifaceted challenges of wireless communications. For example, Ubiquiti's integration of SDN simplifies the deployment, management, and optimization of complex topologies via intuitive graphical user interfaces. Devices like AirCube, AirFiber, and UISP further demonstrate this commitment to flexibility and performance, elegantly fitting into both typical consumer scenarios and demanding industrial applications. Centralized management protocols available through the UniFi ecosystem allow seamless monitoring and control of various network components anywhere from a single cloud-based platform. Enhancements in firmware continuously propel device capabilities forward, with features like long-range point-to-point connectivity and adaptive beamforming no longer mere aspirations, but integral elements of operational functionality. These developments rapidly enhance the deployment of wireless networks even in challenging terrains or congested environments, with AirMAX technology enabling scalable performance not just in horizontal planes but also with vertical sector coverage. Ubiquiti leverages collective user feedback alongside R&D to iterate continually on their offerings, ensuring that devices remain robust, cost-effective, and virtually future-proofed against the constant tide of technological advances. Their bridging of consumer-grade equipment with enterprise prestige empowers network architects to design systems that are both efficient in operation and feasible in cost, ensuring the technology keeps pace with the demand for higher speeds, lower latencies, and robust network security.
Future Directions in Wireless Network Surveys and Technologies
As the digital data landscape continues to expand, the future of wireless network surveys and corresponding technologies promises even greater innovations. Emerging trends in the field are pushing the very boundaries of what wireless engineering can achieve. With the integration of AI-driven algorithms and the rise of machine learning, wireless surveys will become increasingly autonomous, insightful, and predictive, freeing human resources for other critical tasks while enhancing the accuracy of the surveys. Real-time data analytics and adaptive learning will provide networks with the ability to self-configure and self-optimize, instantly reacting to shifts in network demand or interference patterns. Quantum computing looms on the horizon as a disruptive force that may dramatically shift data processing capabilities, opening new horizons for real-time data interpretation in wireless environments. Furthermore, the marriage of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies with wireless networks will demand advanced survey methodologies to accommodate billions of interconnected devices, all requiring stable and reliable network access. As 5G networks develop into 6G, demanding less latency and greater speed, the physical infrastructure, alongside the software for managing this complexity, will evolve, requiring tools like WiFiman to keep pace. Sustainability also plays a role, with developments aimed at reducing energy consumption in network operations without compromising performance. The participation of holographic beamforming and terahertz waves promises to revolutionize how wireless data is transmitted, offering unprecedented bandwidth and speed. The future is not just about connectivity, but about optimized, intelligent, and sustainable wireless environments that respond organically to human and machine needs. Download the app for Android and start your wireless survey adventure today, setting the foundation for futuristic networking experiences. As new frameworks and wireless standards emerge, they will undoubtedly continue to redefine how we engage with and depend on wireless networks, bringing the ultimate wireless survey adventure to reality.
Share Your Opinion
Your Email Will Not Be Published.
All Rights Reserved © Apps Zone 2025
























Kev F
Really helped in placing WAP in house for best coverage. Also use it to detect rogues. Update: it lost the list of names for my devices. Had them a...
Bill C
Three years ago, I had a UNFI access point installed in my home because Verizon had installed their wireless router in a closet in our laundry room...
Mark Abene
Following problem appears fixed now. "Android 14 here. Nice app, but it consistently gets stuck in Scan and I have to force close it. Tap your netw...
A Google user
As an IT specialist that does a lot of customer installs this app is great! I can do a site survey to see which wi-fi channels are currently being ...
A Google user
Incredible! I used to use 3 apps for networks. One for speed tests, one for devices and one for channels. This does it all! Would be perfect if you...