Apps Zone

Understanding Data Analysis in the Digital Age
Data analysis has become an integral component of the digital age, where organizations and individuals are harnessing the power of data to drive decisions and strategies. At its core, data analysis involves systematically applying statistical and logical techniques to describe, condense, and evaluate data. In the context of the digital world, it takes on new dimensions due to the vast volume and variety of data generated every second from various digital sources such as social media, online transactions, smart devices, and more. This data is raw and unorganized, requiring sophisticated tools and techniques to extract meaningful insights. The process begins with data collection, which is the foundational step. Tools such as web crawlers and data scraping technologies are often employed to gather data from web pages and digital platforms. Once collected, data needs to be cleaned and preprocessed to remove any noise or redundant information. This is usually achieved through data wrangling, a critical step that ensures accuracy and reliability of the analysis that follows. In this phase, data analysts must possess a keen understanding of both the domain they are working within and the computational tools available at their disposal. In many modern cases, this includes understanding programming languages like Python or R, which are commonly used for statistical analysis and visualization. Once the data is ready, analytical techniques are applied, ranging from simple descriptive statistics to more complex predictive modeling and machine learning. The latter has become particularly prominent with the advent of artificial intelligence technologies, which allow for smarter decision-making based on the recognition of patterns within massive datasets. Data visualization is another key aspect of data analysis, enabling stakeholders to understand complex data through intuitive graphical representations. Tools like Tableau, Google Data Studio, and Power BI make it possible to create comprehensive dashboards that can instantly convey insights to business leaders or the public at large. These visualizations not only support narrative-driven reports but also help in identifying trends and anomalies that might not be apparent through raw numbers. In a world progressively driven by data, the role of data analysis cannot be overstated, empowering decisions across all spheres from healthcare to marketing and urban planning to financial services.
The Importance of Engagement in Data Sharing
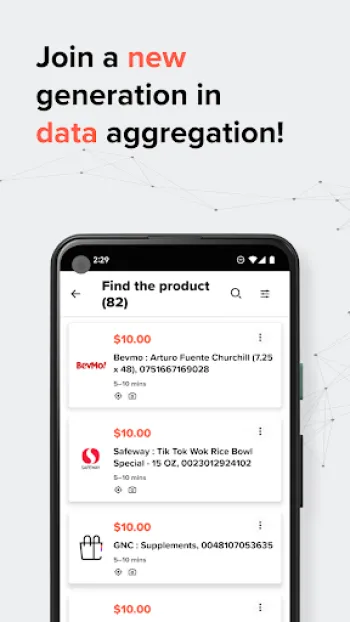
Engagement in data sharing is a crucial element that amplifies the value generated from data analysis. It’s the process where individuals and organizations not just consume analytical insights but also contribute valuable data that can be analyzed. Take the example of city planning; when citizens use platforms like Premise to share local information such as traffic patterns or the location of new construction sites, they are actively engaging in data sharing. This crowdsourced data stands at the intersection of personal experience and community utility, transforming individual observations into collective intelligence that benefits all. Such engagement is not only limited to urban planning but extends to areas like research, where crowdsourced data can help build robust datasets that are otherwise hard to compile. For instance, platforms often provide financial incentives that motivate users to contribute data by taking surveys or snapping photos, thus creating a participatory model of data collection. This engagement model is especially effective in democratic settings where public opinion and participatory governance are encouraged. By involving the community, data collection efforts become more diverse and robust, providing a fuller picture than what might be achieved through limited datasets collected by singular entities. Moreover, engagement through data sharing fosters transparency and accountability. When local communities are involved in data-driven projects, and results are shared back with contributors, trust is built and nurtured, laying the groundwork for long-term collaboration and citizen empowerment. Technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating engagement, with mobile applications offering a convenient interface for users to share and access data. These systems must be designed to simplify participation, ensuring that users with various levels of technical literacy can engage effectively. Considerations around data privacy and security are paramount here, as they build user confidence in sharing data through comprehensive privacy policies and the use of encryption technologies. By fostering a culture of engagement in data sharing, organizations and communities can leverage richer datasets while giving voice to diverse perspectives, ultimately leading to more effective solutions to complex problems.
Technological Tools for Data Analysis and Engagement
The technological landscape for data analysis and engagement is vast and constantly evolving, consisting of a myriad of tools designed to cater to the needs of data analysts and contributors alike. On the analytical side, tools such as Python and R remain foundational due to their extensive libraries for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning. Libraries such as Pandas and NumPy offer efficient data structures and operations for numerical data, while Matplotlib and Seaborn provide powerful capabilities for data visualization. For machine learning tasks, TensorFlow and PyTorch are industry favorites, offering deep learning frameworks that support extensive model customization and scalability. When it comes to handling massive datasets, technologies like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark stand out, providing distributed computing capabilities that can process terabytes of data across clusters of computers. Their ability to quickly sift through large volumes of data makes them indispensable for big data projects. Cloud computing platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer robust environments for data processing and storage, coupled with analytical services that streamline workflows from data extraction to insight delivery. On the engagement end, mobile applications like Premise are pivotal, offering an intuitive platform for users to contribute data effortlessly. Such apps leverage geolocation technology to contextualize data within a geographical framework, enabling more precise and localized insights. They also support multimodal inputs, allowing users to submit surveys, photos, and comments in a seamless manner. Security features embedded within these apps, including two-factor authentication and end-to-end encryption, ensure data is shared safely among contributors and analysts. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provide flexible gateways for connecting different software components, enabling seamless data flow between various tools and systems. This integration is crucial for maintaining data integrity while enabling enhanced functionalities such as real-time data updates and automated reporting systems. The interplay of these technological tools enhances both the analysis and sharing of data, creating a synergistic environment where insights can be generated and disseminated rapidly, efficiently linking data producers to data consumers.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
In the real world, data analysis and engagement find applications across various sectors, demonstrating the transformative power of data-driven solutions. In healthcare, data analysis is employed to track disease outbreaks, predict patient outcomes, and optimize resource allocation in hospitals. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, data-driven approaches facilitated contact tracing, outbreak forecasting, and vaccine distribution strategies that were pivotal in managing the crisis. Patient data collected via electronic health records (EHRs) and wearable devices feed into sophisticated models that predict patient needs and personalize healthcare services. In education, data analysis helps in enhancing learning outcomes by analyzing student performance data to tailor curricula and teaching methods. Learning Management Systems (LMS) track a wealth of data on student engagement and progress, which educators use to identify knowledge gaps and adjust instruction accordingly. In commercial settings, businesses utilize customer data for personalized marketing, inventory management, and sales forecasting. This not only drives profitability through customer satisfaction and retention but also optimizes operations by reducing waste and improving supply chain efficiencies. The public sector too has leveraged data analysis and engagement to drive smarter urban planning and resource distribution. For example, smart city projects use sensor data to monitor and manage traffic, reduce energy consumption, and improve public safety, resulting in more livable urban areas. The application of data analysis in agriculture through precision farming approaches allows for more efficient use of resources and improved crop yields. Data from soil sensors and weather stations are analyzed to optimize planting schedules and irrigation, reducing environmental impact while boosting productivity. These real-world applications underscore the potential of data analysis to revolutionize industries by driving innovations that are both adaptive and predictive, ultimately improving quality of life.
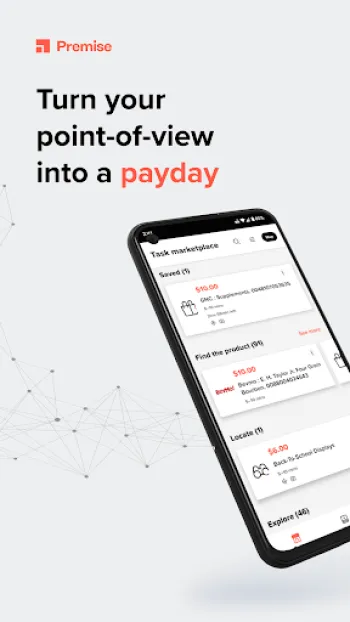
Becoming a Contributor with Premise
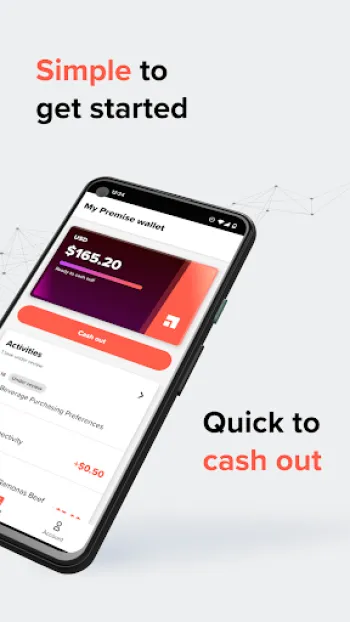
Becoming a contributor with platforms like Premise offers individuals the chance to earn money while simultaneously contributing to a broad spectrum of data-driven projects that benefit local communities and beyond. As a Premise contributor, users engage in diverse tasks that include taking surveys, submitting photos of local events or landmarks, and providing insights into everyday occurrences such as the conditions of roads or the prices of groceries. By capturing these snapshots of reality, contributors feed a continually growing database of localized insights. This data is invaluable for businesses, researchers, and public officials who seek to make informed decisions that reflect real-world conditions. For instance, businesses might use the aggregated data to fine-tune their marketing strategies or understand competitive dynamics in a specific locale. Researchers may leverage this vast repository for academic projects or policy analysis, while governments can integrate these insights into urban development plans or crisis management strategies. The mobile app-based interface ensures that contributing data is accessible to anyone with a smartphone, breaking down previous barriers to participation. With the flexibility to choose tasks suited to their schedule and interests, contributors can easily fit participation into their daily routine, making data collection a part of everyday activities. Financial incentives provided by Premise not only reward contributors for their efforts but also motivate sustained engagement and data quality. The user-friendly design of the app streamlines participation, with step-by-step guides ensuring that even first-time users can navigate the platform effectively. For those interested, downloading the Premise app can be the first step towards not only augmenting income but also making an impact. Contributors can download the application for various platforms: Download for Android. Participating in these endeavors turns data-sharing into a community-driven activity, fostering a culture of cooperative knowledge-building that stands to benefit everyone involved.
Share Your Opinion
Your Email Will Not Be Published.
All Rights Reserved © Apps Zone 2025


























A Google user
Great way to make some extra pocket money! I've used the app for a total of less than 4 hours over several days and have reached ~$12. Cash out lim...
Joshua Cole
Love the app. Easy way to make some extra money. My one issue is the times it reloads items, particularly the Price Monitoring items. For example, ...
Jaycie West
I really love the idea behind this app and even find myself eager to check and see what tasks may be available each day. At first I was able to com...
Katrina Silva
It does pay out if you get enough. With that said though every top dollar task is impossible. Even if you find the item that you're looking for the...
Silvino N.
Changed my data though it isn't working out any more to make it worth while for the next day subjects to get the task fulfilled. Not worth while af...