Apps Zone

Understanding the Fundamentals of VPN Technology and Its Importance for Secure Internet Access
Virtual Private Networks, commonly known as VPNs, form the backbone of modern internet security and transparency, playing a vital role in safeguarding user privacy and enabling unrestricted access to online content. At its core, a VPN works by creating a secure tunnel between the user’s device and the internet, encrypting all data transmissions to prevent interception or intrusion by unauthorized parties. This encryption uses sophisticated algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), which ensures that any data traveling through the VPN tunnel remains confidential and protected against cyber-attacks, hacking, or monitoring by internet service providers (ISPs), governmental entities, or malicious actors. Compared to conventional internet connections, which typically reveal the user’s IP address, location, and browsing habits, a VPN masks this identifying information by substituting the user’s IP with that of the VPN server, thereby anonymizing the user’s digital footprint and significantly enhancing online privacy. From a theoretical perspective, the concept of tunneling protocols such as PPTP, L2TP, OpenVPN, and the more advanced MS-SSTP, the latter of which is integral in the implementation of several highly secure VPNs, constitutes the basis for how encrypted connections are established and maintained. MS-SSTP (Microsoft Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol) utilizes SSL/TLS channels that provide robust security and compatibility with restrictive network environments, effectively bypassing many firewall and censorship restrictions prevalent in geographical regions with heavy internet surveillance. The importance of VPNs extends beyond privacy; they are critical instruments for circumventing geo-blocking and locked content services. By routing connections through servers located in different countries, VPNs allow users to access websites, streaming platforms, and services otherwise unavailable in their region, thereby eliminating digital barriers and achieving an ‘unlimited internet.’ Additionally, businesses depend on VPNs to enable remote work with secure access to internal networks, protecting sensitive corporate data from external threats. The progressive evolution of VPN technology has introduced no-registration, one-tap connection solutions that prioritize user convenience without compromising security. These innovations are exemplified by dedicated servers optimized for regions like Cambodia, where users can experience prioritized server connections that deliver higher speeds, reduced latency for gaming, and an overall smoother browsing experience. Such optimizations reflect the practical application of VPN concepts tailored to serve specific user demographics, highlighting how VPNs have adapted to meet varied internet needs globally. Moreover, compatibility with any type of internet connection—including WiFi, LTE, 3G, 4G, and 5G—ensures that VPNs remain accessible regardless of the user's device or network. This universality is crucial in reinforcing the notion that internet freedom and protection should not be limited by hardware or network type. Understanding these fundamental VPN technologies and their respective advantages elucidates why VPNs are indispensable in safeguarding digital experiences. The combination of encryption, anonymity, tunneling protocols, geographic server selection, and seamless compatibility underpins the operational excellence of modern secure VPN apps. This knowledge serves as a foundation to appreciate the practical ramifications and capabilities of secure, free VPN services designed to provide unlimited internet access.
Technical Architecture and Security Protocols Behind Reliable Free VPN Services
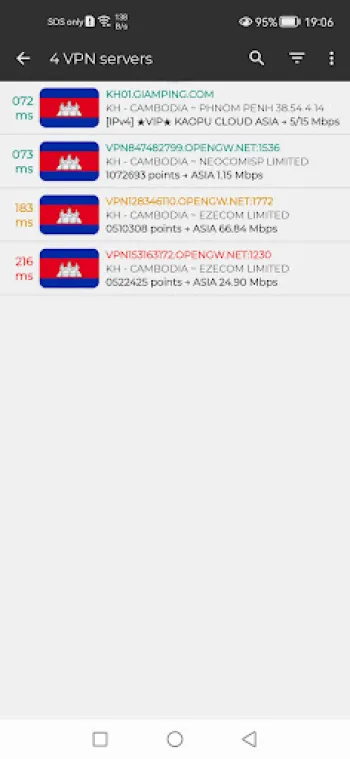
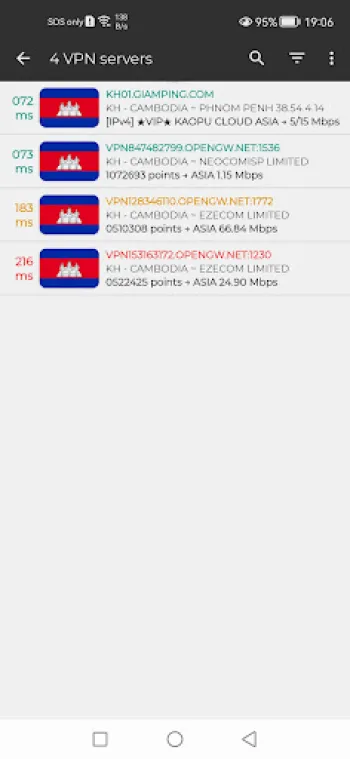
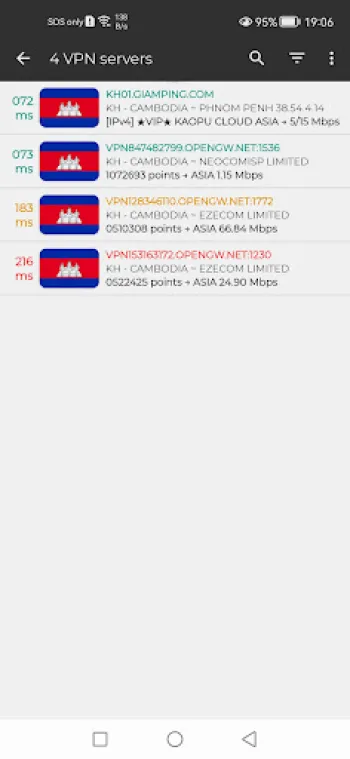
The technical intricacies that constitute a reliable and secure VPN service are multifaceted, incorporating various layers of software and hardware to orchestrate consistent, high-speed, and stable encrypted connections. At the heart of this architecture lie carefully chosen VPN protocols, each offering different balances of speed, security, and compatibility. While older protocols like PPTP provide fast connections, their security vulnerabilities render them obsolete for serious privacy needs. In contrast, protocols such as OpenVPN and MS-SSTP stand out by leveraging SSL/TLS cryptographic frameworks, enabling high levels of data confidentiality and integrity while remaining operable across a wide range of device ecosystems. MS-SSTP, for example, benefits from integration with standard HTTPS traffic, which not only enhances encryption resilience but also facilitates bypassing network firewalls and censorship, as the VPN traffic mimics commonplace secure web browsing data. This is particularly important in environments with restrictive network policies, such as certain educational institutions or workplaces where access to specific websites is denied. Beyond protocols, the VPN's server infrastructure constitutes another cornerstone in the service quality equation. A strategically distributed network of servers protrudes globally, but specialized services often prioritize particular regional servers—such as those in Cambodia—ensuring users experience minimized latency, improved bandwidth, and uninterrupted access. The server configuration must handle enormous concurrent user loads without bottlenecking; this requires scalable hardware with fast SSD storage, high-end CPUs for packet processing, and optimized routing policies that minimize hops and latency. Server-side filtering mechanisms dynamically select optimal servers based on current network performance and congestion levels, ensuring users connect to the fastest, most stable nodes automatically. From a backend perspective, secure authentication methods, including token-based and certificate-based systems, restrict unauthorized access to VPN servers and protect against man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, kill-switch technologies are incorporated to immediately cut off internet access if the VPN connection drops, preventing data leakage beyond the secure tunnel. Complementary features such as DNS leak protection prevent routers or ISPs from circumventing the VPN by leaking DNS requests, maintaining user privacy on all fronts. The ability to filter and direct specific applications through the VPN gateway, known as application filtering, is vital for nuanced control. This capability allows users to designate which apps should use the encrypted VPN tunnel while letting others connect directly to the internet, optimizing bandwidth and ensuring performance where full VPN integration isn't necessary. Security extends to traffic management, where traffic shaping and prioritization optimize performance for gaming or streaming by reducing ping and lag, an essential feature for responsive, real-time applications. With free VPN services, achieving this level of sophisticated infrastructure is challenging due to cost and resource constraints; however, advanced applications now deliver this by leveraging modern cloud platforms, pay-as-you-go server instances, and automated load balancing. These innovations democratize access to secure online experiences, making high-quality VPNs available without subscription fees. Nonetheless, free VPNs must ensure transparency in data policies to maintain user trust, emphasizing no-logging principles and eschewing intrusive ads or data harvesting. Servers also employ advanced firewall rules and DoS mitigation tactics to shield both users and infrastructure from malicious traffic or denial-of-service attacks. In summary, the technical foundation of free, secure VPNs involves a complex orchestration of encryption protocols, robust server architecture, authentication safeguards, traffic filtering, and optimization mechanisms. These components work in unison to deliver seamless, safe, and unlimited internet connectivity to users, safeguarding their data while circumventing regional restrictions and connectivity barriers effectively.
Challenges and Solutions in Providing Unlimited Internet Access via VPNs in Restrictive Regions
Delivering true unlimited internet access through VPNs, especially in regions marked by internet censorship, surveillance, or bandwidth throttling, presents an array of substantial challenges both on the technological and political fronts. Many countries enforce strict measures that regulate internet traffic to restrict access to particular websites or services, often employing deep packet inspection (DPI), IP blocking, or throttling certain protocols to degrade VPN performance. From a technical standpoint, circumventing these impediments requires not just robust encryption but intelligent VPN design capable of adaptive communication strategies. VPN providers combat these challenges by implementing obfuscation techniques that mask VPN traffic to appear as regular HTTPS or other innocuous protocols, thereby evading detection by DPI tools and firewall filters. Technologies such as SSL tunneling and stealth VPN modes are often deployed to facilitate this camouflage. Additionally, deploying a wide array of server locations and rotating IP addresses help prevent blacklistings and enforce uninterrupted service, allowing users to connect through fresh endpoints when traditional ones become blocked or throttled. However, beyond network filters, many ISPs intentionally throttle bandwidth once a VPN connection is detected or after certain thresholds of data usage, deeming it a violation of service policies. VPN services counteract this via traffic optimization, compressing data streams, and improving protocol efficiencies to reduce overhead. Another crucial hurdle is maintaining high-speed connections suitable for data-intensive applications, such as HD streaming or online gaming. Restrictions limiting throughput impose serious constraints. To address this, VPN designs integrate priority routing for gaming servers, low-latency data paths, and smart load balancing between less congested servers to maintain consistent performance. These techniques reduce ping times and packet loss, key determinants in gaming and real-time content consumption. In highly restrictive educational or work environments, firewall configurations might block all non-HTTP traffic and restrict DNS servers, an issue solved through DNS filtering capabilities built into advanced VPN clients. Users can switch DNS resolvers without needing root access, preventing DNS hijacking or leaks, thus retaining secure and uninterrupted browsing. Importantly, the deployment of zero-log policies that do not store user activity details is pivotal; without such policies, users risk exposure if VPN providers are compelled to surrender information under local jurisdiction pressure. Trusted VPN services inherently radiate confidence by foregoing logging entirely, thereby ensuring that even in the event of seizure, user data remains inaccessible. Binding this to application-level filtering capabilities allows users fined-tuned control by channeling traffic from crucial apps like browsers, messaging, or gaming exclusively through the VPN gateway, while less sensitive traffic continues directly, granting a customized privacy and performance balance. Not to be overlooked are regulatory and legal impediments, where some governments ban VPN usage outright or require licenses for providers. Reacting to this, many VPNs maintain flexible business models and architectural agility, such as decentralized server models and support for multiple platforms, to mitigate disruptions swiftly. Consequently, these technical and socio-political challenges drive continuous innovation in VPN algorithms, server structures, and software interfaces. For example, Cambodia VPN Proxy Express embodies these advancements by combining MS-SSTP security with optimized Cambodian servers, providing a practical solution for users facing regional restrictions or ISP limitations. This approach exemplifies how VPNs can transform restricted, censored internet landscapes into open, secure, and boundless digital ecosystems, contributing significantly to digital freedom around the world.
The Role of User Experience and Accessibility in Modern VPN Applications
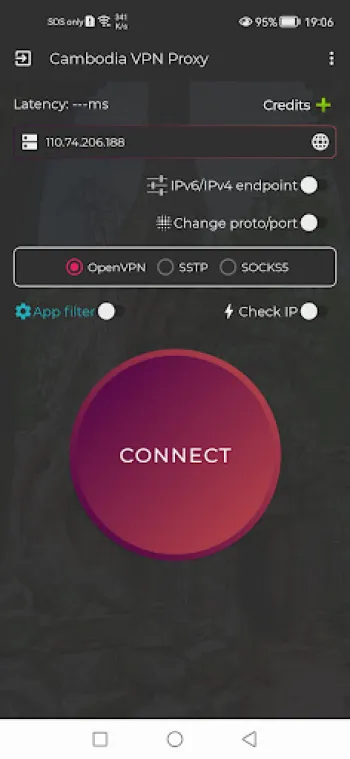
While the underlying technology and security considerations are fundamental to VPN services, the user experience (UX) design and accessibility features hold equal weight in determining the practical success and adoption of VPN applications. Modern users demand VPN solutions that are intuitive, easy to set up, and require minimal technical expertise to operate effectively. This translates to creating interfaces that prioritize simplicity without compromising configurability for advanced users. One key UX feature is the ‘one-tap connect’ functionality, which abstracts complex server selection and protocol negotiation into a single, seamless action for the end-user. Such design diminishes the barrier to entry, encouraging widespread adoption regardless of the user’s technical background. The integration of intelligent server filtering further enhances UX by automatically recommending optimal VPN servers based on geographic proximity, latency, server load, and user preferences. This dynamic selection process ensures users benefit from fast, stable connections without manually cycling through servers. Another crucial component is cross-platform compatibility. Users expect their VPN to work smoothly on diverse operating systems and network types, including Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Linux, and varying mobile data carriers such as 3G, 4G, 5G, or WiFi. Ensuring seamless synchronization and configuration uniformity across such platforms is a complex endeavor but vital for consistent user experience. Additionally, accessibility considerations must span language localization, adaptive text sizes, and UI adaptations for users with disabilities. Transparent performance feedback mechanisms—such as real-time bandwidth usage, connection status, and notifications about connection health—foster user trust and engagement. Privacy assurances embedded within the user interface, like explicit no-logging confirmations and clear privacy policies, empower users to make informed decisions while fostering confidence in the service. The capacity to customize which applications use the VPN via application filters enables users to optimize bandwidth and CPU usage. For example, they can route high-security apps through VPN channels, while letting others bypass it for normal speed and efficiency. As gaming increasingly becomes a popular internet activity, VPNs integrate features like ping boosters and latency reduction tools directly into the app, improving the gaming experience through calculated routing and traffic prioritization. The provision of DNS switching capabilities without requiring rooting devices addresses both security concerns and practical user needs without complicated procedures. Software updates also play a pivotal role in UX excellence. Regular updates address evolving security threats, enhance connection stability, and introduce new features, while maintaining backward compatibility. Automated update systems ensure users are always protected without manual intervention. User-centric support, including FAQs, chatbots, and real-time help desks within the app, contributes to resolving issues promptly, reducing frustrations that can cause users to abandon VPN services. Importantly, balancing ad-supported models or free usage with minimal disruption preserves a premium-like experience even when the service is offered at no cost. In essence, the user experience in VPN applications is the confluence of usability, performance optimization, privacy transparency, and accessibility that altogether transform the complex security protocols and server infrastructures into a reliable, easy-to-use tool that empowers users worldwide to browse safely and privately without limits.
Practical Implementation and Access: Downloading and Using Secure Free VPNs Today
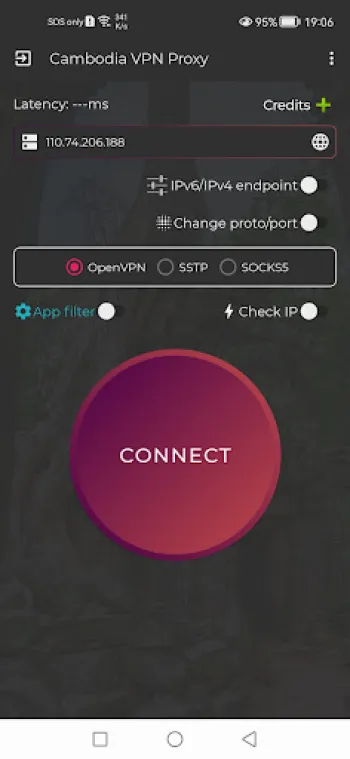
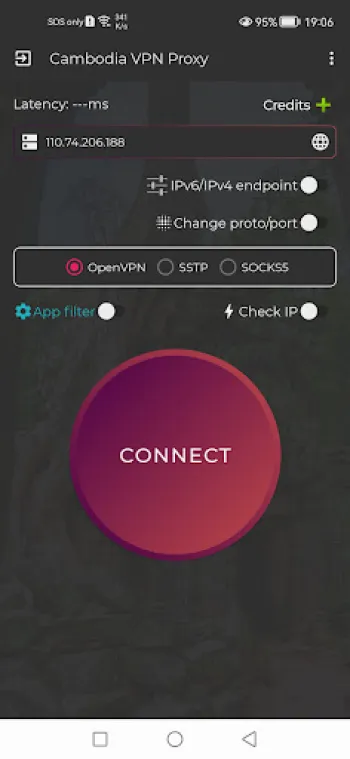
The practical step of acquiring and using a secure, free VPN service is straightforward with well-designed applications that guide users from installation through to establishing their first secure connection. Modern VPN applications, such as those optimized for Cambodia with automatic server filtering, offer streamlined installation experiences that require minimal user input. For Android users, the installation process begins with downloading the app directly from trusted sources to avoid fraudulent versions, exemplified by a simple acquisition via Download for Android. Once installed, the user typically grants necessary permissions, such as network access and the ability to establish VPN connections, after which the app configures the default settings. The onboarding process often includes optional tutorials or tips that explain the significance of features like one-tap connection, application filtering, and ping boosting for gaming. With no registration requirements, users can launch the VPN immediately, eliminating the delay or privacy concerns attached to account creation. This immediate access translates directly to tangible security benefits: all traffic is encrypted using strong protocols like MS-SSTP instantly, instantly shielding online activities from scrutiny by ISPs or attackers. The app also transparently communicates connection statuses and performance metrics to the user, helping them monitor their privacy health. Although for other platforms like iPhone, Windows, Linux, or macOS, specific dedicated versions may not be available or require alternative solutions, many VPNs provide manual configuration guides or compatible protocols to enable secure connections on these devices. Users can leverage third-party VPN clients or built-in OS support, creating custom profiles for MS-SSTP or OpenVPN to achieve similar protection. In addition to providing security and privacy, these VPNs empower users to overcome regional content restrictions and engage with a truly global, unlimited internet—features that are indispensable in today’s fragmented and monitored online ecosystem. Whether seeking higher privacy when browsing, improved latency for online gaming, or uncensored access to social media and streaming platforms, secure VPN applications serve as essential tools. For those concerned about DNS leaks or specific app-based traffic routing, the included DNS switching and application filter modules present advanced options to tailor and optimize their internet experience further. Overall, adopting a secure, free VPN is not merely about downloading software but engaging in an empowered, informed approach to digital rights and internet openness. With ready access from Android platforms and customizable options for other operating systems, users can confidently browse safely and privately without limits, knowing their data is protected by state-of-the-art VPN technology combined with user-friendly application design.
Share Your Opinion
Your Email Will Not Be Published.
All Rights Reserved © Apps Zone 2025



























VKy IN
Cool #.bhi.
Davin kh
Good
Dasis rawana
Good
Sir BLAKE
very good
Lin Htet
LS motor vehicle department and then we will just have