Apps Zone

Background video recorder
Advanced Functionalities and Technical Specifications of Hidden Video Recorders
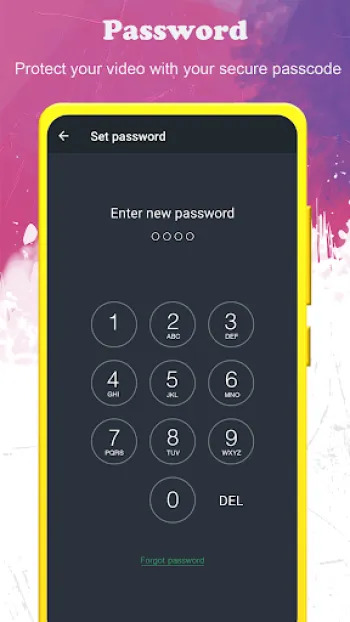
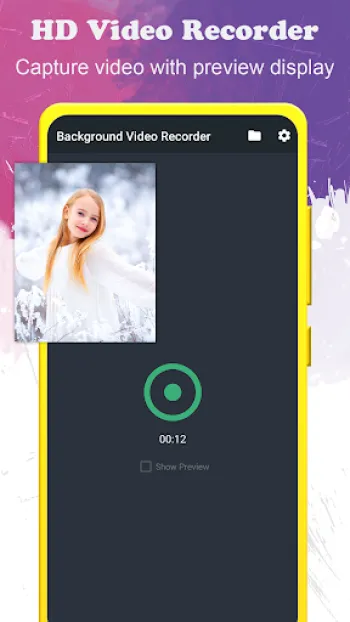
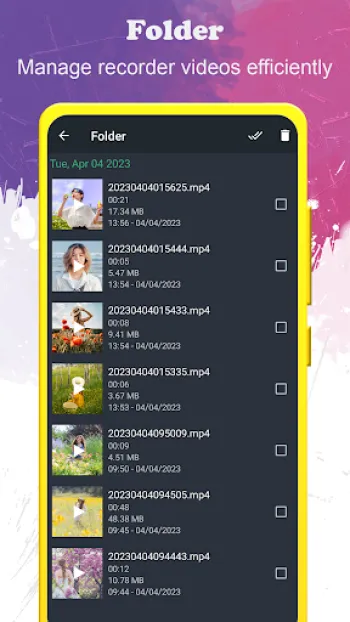
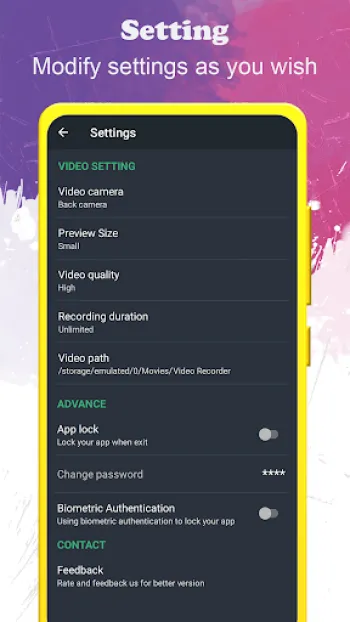
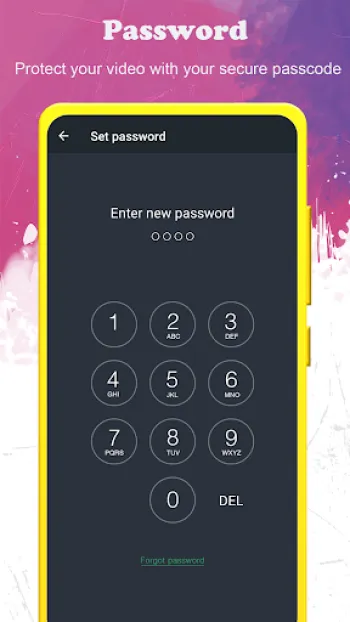
The world of covert recording technology has evolved tremendously, with hidden video recorders now offering a spectrum of sophisticated capabilities that enable users to capture high-quality footage discreetly. The core of these recorders lies in their ability to function seamlessly without alerting subjects or triggering the typical indications of recording, such as preview screens or visible hardware. Technically, these devices and software operate by harnessing advanced codecs that compress video in real-time, allowing for extended filming durations without compromising resolution. Typically, an app designed as a background video recorder utilizes hardware acceleration and software optimization to manage processing loads efficiently. This optimizes battery consumption and ensures that the recording can continue even when other applications or system functions consume bandwidth or power. Furthermore, these applications can employ dynamic bitrate adjustment algorithms that regulate the quality of video output based on ambient conditions such as lighting and motion intensity, thus producing consistently clear images while balancing storage constraints. In terms of video quality, full HD recording (1920x1080) represents a baseline standard in contemporary hidden video recorders, enabled by support for modern sensor technology and digital image stabilization. This reduces the blurriness associated with hand movements or device vibrations and maintains clarity that is crucial for identification and evidence gathering. Multifaceted orientation support means that users can record videos in portrait or landscape modes depending on the situation, with the software automatically adjusting encoding parameters to maintain aspect ratios and minimize artifacts. The option to record without preview screens or UI distractions is critical in maintaining discretion. This invisibility is typically backed by background service running in the operating system, which can keep the camera active without rendering a live view. Security layers such as passcode locks are integrated within the app framework to prevent unauthorized access, ensuring that the captured data remains confidential. Some advanced models and apps also incorporate encrypted video file generation to further bolster privacy. Another technical highlight is the capability to function during phone calls—a feature that requires in-depth integration with the phone’s modem and audio subsystems to avoid interference or system warnings. This dual recording feature can be invaluable for investigative or protective purposes where multi-channel capture is required. Marginal aspects like free storage checks guarantee that recording sessions do not unexpectedly terminate due to lack of space, which is a function managed by querying the device’s file system APIs in real-time. Moreover, support for external SD cards is especially beneficial for users filming lengthy or high-volume footage, facilitating easier offloading and backup options. The interface design typically prioritizes one-touch accessibility; users can initiate or halt recording processes with minimal screen interactions, often by using shortcuts such as notification toggles or floating widgets, which further reduce the visual footprint of the app. This technical architecture is matched by a focus on cross-lingual support, enabling usage across more than 50 languages, thereby expanding accessibility globally. Overall, the fusion of hardware utilization, sophisticated software engineering, and end-user convenience defines the excellence in modern hidden video recorders.
Practical Applications and Use Cases in Various Fields
Hidden video recorders with high-quality capture capabilities have found essential roles in multiple real-life contexts, transcending mere novelty or personal curiosity to become indispensable tools in professional, security, and journalistic domains. In law enforcement and private investigation, for example, covert recording allows for unobtrusive evidence collection during surveillance or undercover operations, ensuring that suspects remain unaware of monitoring activities, thereby preserving the authenticity of behaviors captured on camera. Investigators can use such devices to document interactions or illicit activities without the risk of alerting subjects, which could compromise investigations. This is especially vital in sting operations or when gathering proof of workplace misconduct where visible cameras might be tampered with. In the realm of personal security, hidden video recorders prove crucial for recording incidents such as harassment, abuse, or theft without provoking the aggressor. Individuals can record interactions discreetly, using standard devices such as smartphones equipped with background recording apps; this footage can later serve as concrete evidence in legal proceedings, providing a layer of personal protection that goes beyond verbal testimony. Journalists and activists in restrictive environments also heavily rely on hidden cameras to document events, interviews, or protests without drawing attention. The ability to operate in stealth mode is a protective mechanism against censorship or retaliation, ensuring stories reach public attention while safeguarding the recorder’s identity. Moreover, teachers or employers might deploy such technology for monitoring purposes while maintaining ethical boundaries – for instance, to ensure compliance with safety regulations, prevent bullying, or verify employee conduct. In consumer settings, hidden video recorders facilitate activities such as wildlife observation, where a visible camera would disturb natural animal behavior. The high-definition nature of recordings enables biologists or hobbyists to analyze movements or identify species in their habitat without intrusion. Parents and caretakers might use these devices to monitor childcare environments covertly, ensuring the well-being of infants or elders in absence, while maintaining normalcy and avoiding distress caused by overt surveillance. Another compelling use case is in creative arts; documentary filmmakers or performance artists experiment with hidden video applications to capture candid moments or authentic reactions that traditional filming might compromise. This spontaneity enriches storytelling with unfiltered emotional layers or social dynamics. Technically sophisticated recorders also empower security personnel to maintain round-the-clock surveillance within sensitive areas without revealing cameras that could be disabled or avoided. Since many hidden video recorders support recording while the device screen is off, this extends operational time and reduces the chances of detection through visual cues like screen illumination or button interaction sounds. Additionally, business owners may utilize such covert recording solutions to deter shoplifting or monitor overall store security discreetly, balancing customer privacy with loss prevention. Of course, the operational parameters, such as recording duration, orientation, and camera selection—front or back—allow users to tailor solutions specific to their situational needs, whether that involves capturing distant occurrences with a rear camera or recording interactions from the front camera while positioning the phone naturally. Importantly, hidden video recorders provide an ethical gray area that requires awareness of legal limitations in diverse jurisdictions, necessitating users to inform themselves about boundaries regarding consent and privacy before deployment to avoid infractions. Such recorders, particularly available as applications on smartphones, merge convenience with effectiveness, transforming everyday devices into versatile surveillance tools accessible to wide audiences, expanding their impact across security, research, and creative endeavors.
Operational Challenges and Solutions in Background Video Recording
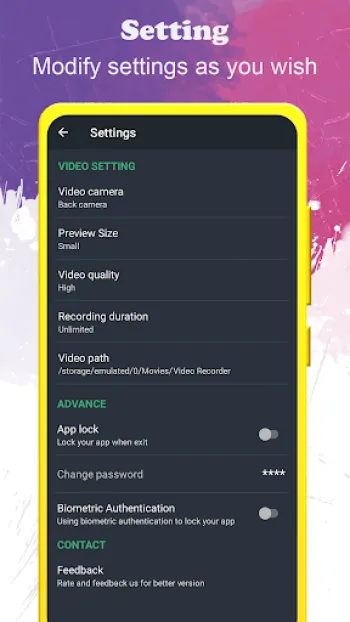
The hidden video recorder ecosystem faces a variety of intricate operational challenges due to the need to balance stealth, performance, and legal compliance. Primary among these is managing device resources without alerting users or bystanders. Video recording is inherently resource-intensive, involving continuous sensor activation, real-time encoding, and considerable write speeds to storage media. Running these tasks clandestinely demands optimization of CPU cycles and memory usage to evade system triggers that could indicate excessive activity, such as overheating warnings or unusually fast battery drainage that might signal covert operations. Developers achieve this by leveraging native hardware acceleration features like GPU encoding and dedicated image signal processors (ISP) to offload workloads from main processors, thereby maintaining overall device responsiveness and energy efficiency. Another core technical challenge is managing the user interface invisibility while ensuring operational control. Apps must avoid displaying camera previews or record indicator lights, which typically inform users that recording is active. This requires the app to operate largely in background mode with minimized notification cues, yet remain accessible enough to start or stop recordings reliably. To solve this, apps integrate with system notification frameworks offering discreet controls embedded in the status bar or use gesture-based shortcuts invisible to casual observers. Handling interruptions such as incoming calls, alarm triggers, or app switching presents additional complexity. The app must seamlessly pause or continue recording without user intervention, maintaining file integrity and avoiding corruption. This requires robust lifecycle management within the operating system, employing listeners and broadcast receivers to monitor various system events and adjust recording states accordingly. Storage management is equally critical, as video files can consume large amounts of space quickly. Implementing real-time free storage checks prevents sudden halts mid-recording, which would compromise captured evidence. Offering support for external SD cards extends capacity, but also introduces challenges such as SD card compatibility, managing removable storage permissions, and handling scenarios where the card is removed during active recording. Regarding privacy protection, ensuring recorded files and app access remain secured is paramount. Without proper encryption and passcode protections, videos risk unauthorized exposure. Thus, the integration of secure file handling, encrypted folders, or self-destruct options on failed authentication attempts underscores the importance of maintaining confidentiality. User education also forms part of addressing operational challenges; a technically advanced app might overwhelm casual users without simple and clear configuration paths, leading to misuse or failures in stealth functionality. Hence, UX designers emphasize intuitive layout, brief tutorials, and minimal parameters required to operate effectively while retaining flexibility for advanced adjustments such as video orientation or scheduling recordings. Lastly, compliance with platform policies—especially on Android and iOS—imposes strict limitations on background camera activity due to privacy concerns, requiring developers to stay updated with API changes, permissions frameworks, and user consent requirements. Innovative solutions include embedding background video recorders within multi-feature apps to disguise their functionality under legitimate use cases or leveraging accessibility permissions to gain nuanced camera access without drawing scrutiny. These operational hurdles reflect a sophisticated interplay between hardware capabilities, software design, system-level policies, and user expectations, with continuous improvements pushing the boundaries of what hidden recording applications can achieve without detection.
Comparative Analysis of Hidden Video Recorders versus Conventional Cameras
The distinction between hidden video recorders and conventional camera systems primarily derives from design intention and operational context, manifesting in differing priorities that affect usability, functionality, and technical constraints. Conventional cameras, whether standalone digital devices or smartphone cameras, focus predominantly on maximizing video fidelity, user control, and ease of preview. They feature visible hardware elements such as prominent lenses, physical buttons, and active screens that provide real-time feedback on framing, focus, and exposure. These characteristics are essential for professional photography or videography but counterproductive in covert scenarios where visibility compromises the purpose. Hidden video recorders, by contrast, emphasize invisibility and non-intrusiveness over direct user feedback. In practice, this demands compromises such as the absence of live preview windows or on-device displays, which necessitates reliance on pre-configured settings and indirect control methods. This trade-off often results in a learning curve during setup but ensures stealthy operation. Technically, hidden recorders incorporate streamlined user interfaces designed to minimize interactions, often enabling one-touch or scheduled recordings without manual adjustments during shooting. Whereas conventional cameras react instantly to user inputs with visible confirmation, hidden recording apps operate silently, interfacing with the operating system to suppress normal indicators such as shutter sounds or on-screen recording icons. In terms of video quality, conventional cameras often benefit from larger sensors, interchangeable lenses, and superior optics, yielding higher dynamic range and low-light performance. Hidden recorders tend to rely on built-in phone cameras or smaller sensors to maintain compactness and concealment, which can limit image quality under challenging conditions. However, advances in computational photography, such as AI-enhanced noise reduction and adjustable encoding parameters, have narrowed this gap significantly, enabling hidden recorders to produce sufficiently high-quality footage for most practical applications. Battery life and recording duration also differ markedly; standalone cameras, particularly professional models, often incorporate substantial batteries and dedicated cooling systems, facilitating prolonged recording sessions. Hidden video recorders, constrained by the host device’s resources, must optimize for power efficiency and thermal management to avoid rapid depletion or overheating, especially when recording in the background with the screen off. The capability of hidden recorders to function during other phone activities—like handling calls and background app usage—is a clear advantage in surveillance contexts, whereas conventional cameras require standalone operation, sometimes necessitating additional recording gear or storage media. Another point of divergence lies in legal and ethical considerations; conventional cameras, visible to all, implicitly inform subjects of recording, aligning with privacy norms. Hidden video recorders walk a finer line, necessitating users’ awareness of consent laws and usage contexts. This dual aspect influences app design, embedding features such as access restrictions, password protection, and discreet operation modes to balance utility and privacy compliance. From a cost perspective, hidden video recorder apps represent a low-barrier entry point, often available as cheap or free downloads, whereas professional hidden cameras or espionage equipment can be expensive and complex to operate. This accessibility democratizes covert recording but necessitates user caution regarding ethical and technical reliability. In conclusion, while conventional cameras excel in transparent, controlled recording environments prioritizing image quality and user interaction, hidden video recorders distinguish themselves by enabling stealth, background operation, and integration with multifunctional devices, making them uniquely suited for surveillance, personal security, and investigative use cases where discretion is paramount.
The Future of Hidden Video Recording Technology: Trends and Innovations
Looking forward, hidden video recorder technology is poised to benefit from multiple converging advancements in hardware miniaturization, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, promising to redefine the boundaries of covert video capture with enhanced capabilities and ethical safeguards. One prominent trend is the integration of AI-powered real-time video analysis during recording. Future hidden video recorders will not only capture high-definition footage but also process data on-device to detect specific objects, faces, or behaviors autonomously. This will allow users to receive alerts or automated tagging without the need for post-processing, significantly improving the efficiency of monitoring surveillance footage. Edge computing advances, combined with deep learning models optimized for mobile hardware, will support smarter recording triggers—capturing only relevant footage when motion or designated patterns arise. This selective recording capability will reduce storage requirements and improve privacy by avoiding unnecessary or irrelevant video capture. Simultaneously, hardware improvements in sensor technology promise higher sensitivity in low-light and variable lighting environments. Emerging camera modules incorporating stacked CMOS sensors and multi-spectral imaging could enable hidden recorders to detect details invisible to the naked eye, extending usefulness in security and scientific applications. Enhanced optical zoom through variable focal length lenses that maintain a compact form factor will support wide-ranging covert video capturing scenarios. Additionally, the evolution of flexible electronics suggests the possibility of embedding cameras into previously impossible form factors, such as thin films or textiles, creating wearable hidden recorders that blend naturally into clothing or accessories. The synergy between such hardware and AI algorithms will empower contextual awareness, enabling devices to distinguish between normal and suspicious activity autonomously. On the software side, future developments will emphasize encrypted cloud backups with zero-knowledge privacy guarantees, so that hidden videos can be securely stored and accessed remotely without compromising user anonymity or content integrity. Blockchain-enabled timestamping of recorded videos may provide indisputable proof of authenticity for legal or journalistic use. User experience enhancements will likely include voice-activated recording commands and intelligent scheduling based on learned user habits or environmental cues, minimizing manual intervention while maximizing operational stealth. Furthermore, ethical transparency will gain prominence as regulatory frameworks mature globally. Built-in compliance modules could alert users on legality boundaries per region or restrict usage accordingly, fostering responsible deployment of such powerful technology. Privacy-preserving anonymization features, such as automatic face blurring or audio muting, may be integrated as standard to balance security needs with societal norms. In the context of multi-device ecosystems, hidden video recorders might leverage IoT connectivity, linking with smart home systems, drones, or body-worn devices to create synchronized surveillance networks that offer comprehensive situational awareness. These networks would feature adaptive recording modes that distribute loads intelligently, preserving battery and storage while maximizing coverage. Ultimately, the convergence of hardware miniaturization, AI intelligence, secure cloud integration, and ethical oversight heralds a future where hidden video recorders become smarter, more reliable, and more responsible instruments for covert video capture. As these trends unfold, users will benefit from greater control, enhanced quality, and deeper insights, empowering their applications in personal security, professional investigations, and beyond. Interested individuals can explore current solutions by exploring cutting-edge apps that embody many of these features; for Android users, an excellent starting point is to Download for Android, which encapsulates many of the discussed innovations such as background recording, front and back camera compatibility, and encrypted app security.
Share Your Opinion
Your Email Will Not Be Published.
All Rights Reserved © Apps Zone 2026























Work4dough
Works good but doesn't record for more then 30min. Even if it says in the saved file 45 minutes was recorded or whatever. It's actually only 30min ...
kashif imran
It is very useful.records everything without showing on screen 5minuted restriction recording is not very good sign now I HV bought it for life tim...
Christo Van Der Sandt
Very impressed. awesome. Is there anyway you can upgrade the video or maybe do some sort of night vision?
Martin Lopez
It has worked fine for me. It's free, your videos don't appear in your gallery. Some ads but not too bad. It records for a long time. 45 minutes th...
Damien Kroyal
Having trouble playing a video. I used the app to record the audio for a 46 minute class, and I think it may be too long, or my phone may not have ...