Apps Zone

VPN UAE - Private & Secure VPN
Understanding VPN Technology and Its Role in Secure Internet Browsing
Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology is an indispensable tool in today's digital landscape, allowing users to create a secure and encrypted connection over less secure networks such as the public internet. At its core, a VPN acts as a private tunnel between a device and the internet, masking the user's IP address and encrypting data packets to ensure privacy and security against eavesdropping, hacking, and tracking. This technology involves complex protocols like OpenVPN, WireGuard, and IKEv2, which operate using various encryption standards including AES-256, regarded as bank-level security. The significant advantage of VPNs lies in their capacity to bypass geographical and administrative restrictions, enabling users to access websites and services blocked due to censorship or geo-fencing. The process involves routing internet traffic through intermediate servers located in diverse regions worldwide, effectively cloaking the users’ original digital footprint. For instance, a user based in the Middle East trying to access content exclusively available in the US can utilize a VPN server located in America, which assigns a US-based IP address, granting unhampered and anonymous access to the desired website. Beyond this functionality, the encryption safeguards against third-party surveillance, whether by ISPs throttling bandwidth based on content or malicious actors attempting man-in-the-middle attacks. On a theoretical level, the VPN leverages tunneling protocols like GRE and IPsec to encapsulate data packets, adding layers of security and integrity verification. Practically speaking, this means that all communications from instant messaging to financial transactions remain confidential and discreet. The technology is highly relevant for both personal privacy and organizational security policies, especially with the increasing prevalence of remote workforces requiring secure access to corporate resources. Additionally, the zero-log policy prevalent in reputable VPN services guarantees that user activity metadata is not stored, thereby enhancing security against data breaches or governmental subpoena. Users must understand that VPN performance hinges on server distribution and infrastructure robustness; a VPN service with over 1000 servers globally, like many advanced offerings today, ensures low latency, high throughput, and minimal packet loss, contributing to seamless streaming, gaming, and browsing experiences. The evolution of VPNs further integrates advanced features such as split tunneling, kill switch mechanisms, and DNS leak protection, reinforcing security without compromising usability. Hence, a VPN serves as both a shield and a key—shielding users from digital threats while unlocking a freer, faster internet.
The Importance of Speed and Stability in VPN Services for Unblocking Websites
Speed and stability are pivotal attributes of an effective VPN, particularly when the objective is to unblock websites and platforms that impose strict access controls or carry high bandwidth demands such as streaming services and online gaming environments. The underlying infrastructure must include a vast network of geographically dispersed servers with optimized routing to avoid latency spikes and connection drops. For example, a VPN service optimized with over a thousand servers distributed worldwide allows users to select locations that minimize physical distance and network congestion, directly impacting download and upload speeds. From a technical perspective, VPN protocols have varying impacts on speed; WireGuard, for instance, is renowned for its streamlined codebase and rapid handshake process, delivering faster connection times compared to the more established OpenVPN. Stability is ensured through dedicated servers with reliable bandwidth allocation and failover mechanisms to prevent sudden disconnects—crucial when accessing platforms like Netflix or Disney+, where interruptions could disrupt streaming continuity. Additionally, advanced load balancing systems manage user traffic, reducing the chance of server overload and bottlenecks during peak periods. This is especially beneficial when accessing restricted content in real-time, such as participating in PUBG mobile gaming or engaging with other fast-paced applications requiring low ping and jitter. Importantly, VPN stability also involves resistance to traffic shaping and throttling implemented by ISPs; by encrypting data packets, a well-implemented VPN obscures traffic patterns, circumventing ISP throttling that otherwise would degrade streaming quality or increase latency. Real-world examples highlight that without such robust speed and stability, users encounter buffering, delayed game response, and interrupted downloads, which detracts from the overall user experience. Moreover, zero-log policies coupled with strong encryption prevent data compromise without introducing delays, ensuring user activities remain confidential without sacrificing performance. Continuous monitoring and server updates maintain optimal operation standards, and users often benefit from intelligent server selection tools that automatically connect them to the fastest available node. The synergy of speed and stability in VPN services directly correlates with user satisfaction and the capacity to seamlessly browse geographically restricted websites, thereby reinforcing the crucial role these factors play in contemporary VPN applications.
Advanced Encryption and Security Protocols Ensuring Privacy and Data Protection
At the heart of every reputable VPN service lies sophisticated encryption and security protocols that define its ability to protect user privacy and secure sensitive data transmissions. Modern VPNs employ encryption algorithms such as AES-256, which is endorsed by the National Security Agency (NSA) for securing classified information, providing a virtually unbreakable cipher framed within symmetrical key cryptography. Encryption not only scrambles data but also incorporates authentication and integrity verification methods protecting against packet interception and tampering. Key exchange mechanisms like Diffie-Hellman and Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman ensure that session keys are securely negotiated without direct transmission, further eliminating risks of interception during connection establishment. VPNs utilize multiple protocols, including OpenVPN (which uses SSL/TLS), IKEv2/IPsec for rapid and resilient reconnections, and WireGuard with its minimalistic architecture designed to maintain high security with performance efficiency. These protocols guard against an expansive range of threats, including man-in-the-middle attacks, IP and DNS leaks, and potential hijacking attempts. Advanced VPN offerings integrate features like a kill switch, which instantly severs internet connectivity if the VPN tunnel fails, guarding against accidental exposure of user IPs. Parallel to this, DNS leak protection ensures DNS queries—that can reveal browsing activities—are routed securely through the encrypted tunnel without leaking to external resolvers. Importantly, zero-logging policies enhance privacy by refraining from storing any metadata or activity logs, making it impossible for any third parties, including authorities or hackers, to trace the user's online behavior. From a theoretical standpoint, this approach aligns with privacy principles such as data minimization and pseudonymity, which are critical in environments where surveillance risks are high. Practically, combining these encryption techniques and protocols means users can safely access global content without fear of data breaches or unauthorized tracking. For instance, journalists, activists, and everyday users alike benefit from these measures when circumventing censorship or conducting confidential communications. Even when connecting through insecure networks such as public Wi-Fi hotspots, users remain shielded against common cyber threats due to the robust VPN encryption layer. The technological maturity and continual updates to cryptographic standards reaffirm the pivotal role of advanced encryption and security protocols in enabling a VPN to confidently assert itself as a bastion of privacy and trustworthiness in an increasingly surveilled digital realm.
Unblocking Restricted Content: How VPNs Circumvent Censorship and Geo-Restrictions
One of the VPN’s most sought-after functionalities is its ability to circumvent geographical restrictions and censorship, effectively unblocking websites and applications that are otherwise inaccessible due to governmental policies, content licensing agreements, or targeted network restrictions. These blocks manifest through various techniques such as IP blocking, DNS filtering, and deep packet inspection (DPI). VPN services counter these tactics by assigning virtual IP addresses corresponding to the server location selected by the user, thereby masking the user's true location and allowing access to region-specific content. For example, streaming platforms such as Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ restrict content libraries based on licensing agreements; users from unsupported countries can bridge these limitations by connecting to VPN servers where these services are available, enabling full access to movies and series irrespective of their real-world geographic position. Technically, this involves encapsulating data packets that resemble legitimate traffic and routing them through secure tunneling protocols, which evade DPI methods used by censors that scrutinize traffic patterns to identify and block VPN usage. Intelligent obfuscation techniques, including XOR encryption, stealth VPN modes, and the use of VPN protocols such as Shadowsocks, enhance the ability to remain undetectable on networks with authoritarian firewalls like the Great Firewall of China or those deployed in countries with strict internet surveillance. Moreover, VPN providers often rotate IP addresses and maintain server farms in multiple countries to reduce the likelihood of their servers being blacklisted by content providers or local ISPs attempting to enforce restrictions. This dynamic infrastructure ensures users can continually access blocked platforms such as popular social media networks—Instagram, Snapchat, Twitter, Facebook, WhatsApp—and video sharing services like YouTube, which might be censored or restricted in some regions. On a practical level, this guarantee of freedom to browse without hindrance translates into enhanced access to global information, educational resources, cultural exchange, and unrestricted business operations. For businesses operating across borders, VPNs facilitate remote access to local intranets, e-commerce sites, and critical cloud services unimpeded by region-based internet segmentation. Furthermore, unblocking technologies also improve user experience in competitive gaming, avoiding regional bans or lag spikes by maintaining optimal routing and location spoofing. Thus, the VPN’s capacity to break through digital barriers creates a more open internet environment, fostering the democratization of information and communication across traditional geopolitical and regulatory divides.
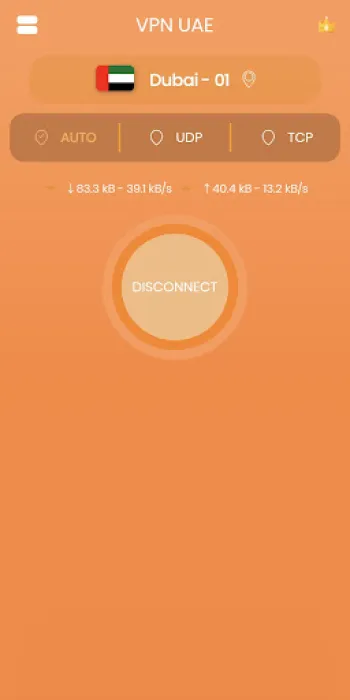
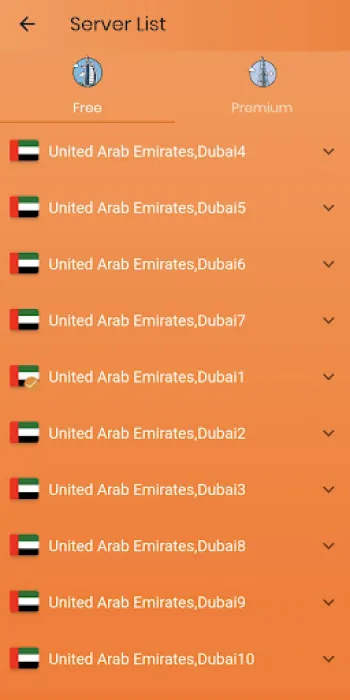
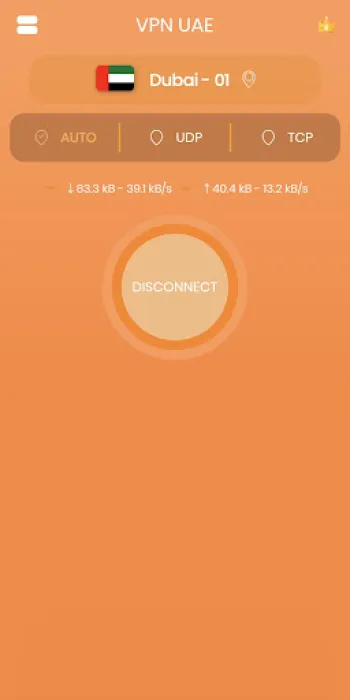
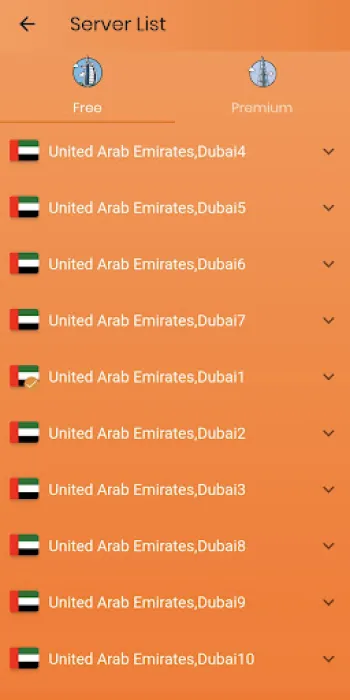
Practical Implementation and Usage of VPN UAE: Accessibility and User Support
Implementing a robust VPN solution like VPN UAE Free involves both accessible design and comprehensive user support, ensuring that users—from novices to tech-savvy individuals—can effortlessly benefit from secure and unrestricted internet access. This VPN requires no prior registration, instantly reducing barriers to use and privacy concerns associated with account creation, thereby simplifying setup to a single-step process. The availability of VPN UAE across platforms such as Android offers seamless integration with mobile devices, catering to the dominant modes of internet connectivity in many regions. Users can quickly and reliably connect to any of the 1000+ servers worldwide, with each server optimized for stability and speed. The simple and intuitive interface minimizes configuration requirements, automatically selecting the best server based on location and network conditions while allowing manual overrides for advanced users seeking specific regional endpoints. From a technical standpoint, VPN UAE employs leading bank-level encryption standards, incorporating advanced protocols that secure data transmissions without noticeable latency or performance degradation. Its dedicated servers support bandwidth-intensive activities such as streaming HD content on platforms like Netflix and Hulu or speeding up online gameplay by reducing ping times in PUBG and similar titles. The commitment to zero-logging policies is a critical component that aligns with the privacy expectations of users wanting assurance their activity remains confidential. Support structures are in place to provide timely user assistance, with dedicated teams ready to resolve connectivity issues or address technical challenges, enhancing customer satisfaction and trust. Practical examples of VPN UAE’s utilization include users bypassing workplace firewalls restricting social media access or circumventing censorship in high-surveillance environments, enabling free information flow and communication through standard applications like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger. Furthermore, its adaptive server network, resilient against throttling and ISP interference, guarantees that internet performance remains smooth and unrestricted. For those seeking to enhance their internet experience with a reliable and secure VPN, this solution offers direct download options such as Download for Android, facilitating immediate access to a safer and faster browsing environment. While iPhone, Windows, Linux, and Mac versions are continually developed, the current focus on the Android platform exemplifies an effort to meet the needs of a vast user base seeking dependable VPN connectivity in a privacy-conscious manner.
Share Your Opinion
Your Email Will Not Be Published.
All Rights Reserved © Apps Zone 2026



























Isiphile Matiwane
best VPN I like it
Nolukholo Hlanga
i like this app but to me it doesn't want to disconnect what must I do please help,I really want to use it.
M Ashraf
best vpn i have ever use .
Thandokazi Klaas
I recently downloaded this app but I don't really know how it works
Asmer Mehmood
good VPN I am enjoying